Targets
Paris Agreement targets
NDC description
Russia formally submitted a new 2030 emissions target to the UNFCCC in November 2020. The update did not strengthen the country’s 2030 target in any real sense, as it is higher than Russia’s own 2030 emissions projections under current policies.
Russia’s updated 2030 target of a 30% reduction below 1990 levels, which replaces its previous target of 25-30%, amounts to a 2030 emissions level of 2.4 GtCO2e (24% below 1990 levels, excluding LULUCF). Given the latest emissions projections under current policies provided by the Russian Government show 2030 emissions at 2.3 GtCO2e (excluding LULUCF), this does not represent a real cut to emissions.
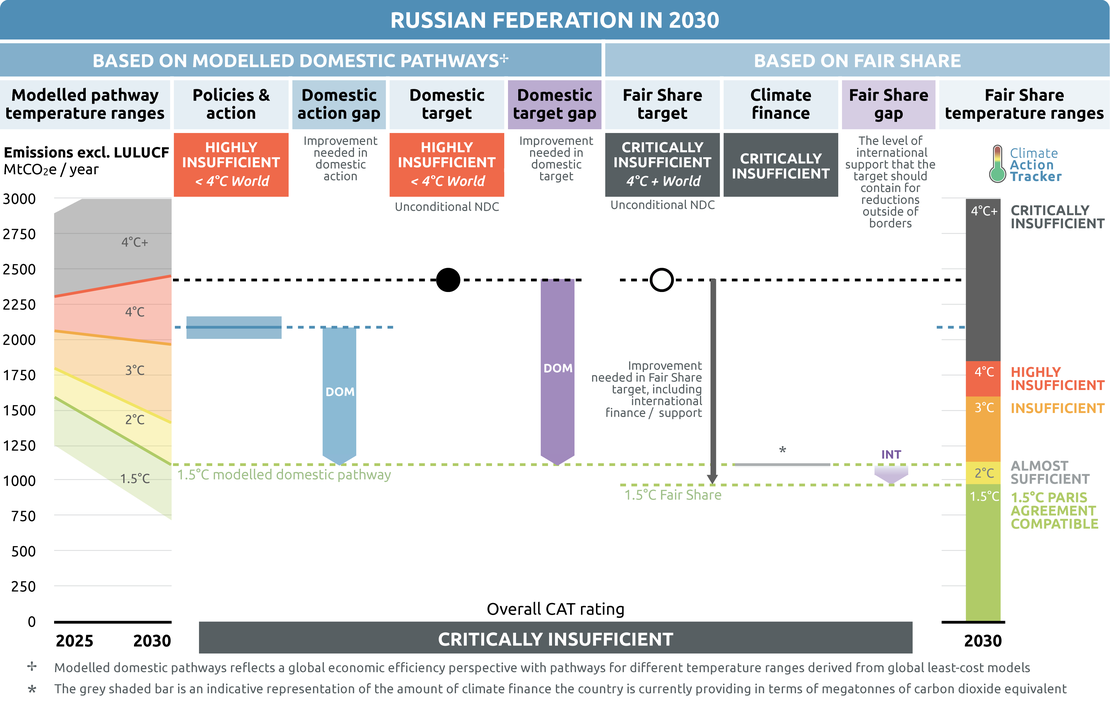
The CAT rates Russia's target as "Highly insufficient" when rated against modelled domestic pathways ("domestic target"), and "Critically insufficient" when rated against its fair share contribution ("fair share target"). Russia has not specified an international element in its NDC, so we rate the target against the two rating frameworks.
We rate Russia’s updated 2030 emissions target; at least a 30% reduction below 1990 levels (incl. LULUCF), as “Highly Insufficient” when compared with modelled domestic emissions pathways. The “Highly insufficient” rating indicates that Russia’s domestic target in 2030 leads to rising, rather than falling, emissions and is not at all consistent with the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C temperature limit. If all countries were to follow Russia’s approach, warming could reach over 3°C and up to 4°C.
We rate Russia’s updated 2030 emissions target as “Critically insufficient” when compared with its fair-share emissions allocation. The “Critically insufficient” rating indicates that Russia’s fair share target in 2030 reflects minimal to no action and is not at all consistent with the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C temperature limit. Russia’s target is not in line with any interpretation of a fair approach to meeting the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C limit. Substantial improvement is needed. Some of these improvements should be made to the domestic emissions target itself, others could come in the form of additional support for emissions reductions achieved in developing countries in the form of finance. If all countries were to follow Russia’s approach, warming would exceed 4°C.
Russia’s international climate finance is rated as “Critically Insufficient” (see below) and is not enough to improve Russia’s fair share rating.

Russia’s international public finance contributions are rated as “Critically Insufficient”. Russia has not made any substantial contribution to international climate finance since the adoption of the Paris Agreement. To improve its rating, Russia needs to urgently increase its financial contributions and stop funding fossil fuels abroad.
Russia has committed to provide a total of USD 10 million in climate finance from 2020-2022 to the Green Climate Fund (Green Climate Fund, 2020). Even considering this recent commitment, contributions remain critically insufficient considering the size of Russia’s economy and its historical responsibility.
Russia actively finances fossil fuels abroad, including coal, such as in the Long Phu 1 Coal Plant in Vietnam (EndCoal, 2020).
Further information on how the CAT rates countries (against modelled domestic pathways and fair share) can be found here.
Last NDC update
Russia has updated its NDC, but did not increase ambition.
Russia’s new NDC is stronger on paper, but does not alter the real-world trajectory of its emissions. Russia’s own emissions estimates show current policy emissions projections in 2030 below its new target. Maintaining the same level of real-world emissions in 2030 breaks the Paris Agreement’s requirement that each successive NDC should represent a progression beyond the current one.

Net zero and other long-term target(s)
In March 2020, Russia released its draft long-term climate strategy (Russian Federation, 2020a), which outlined two sets of emissions projections to 2050; a “baseline” scenario, which results in 26% higher emissions than 2017 levels (36% below 1990 levels), and an “intensive” scenario, which results in an emissions level 3% higher than 2017 levels (48% below 1990 levels). The strategy recommends adoption of the less ambitious “baseline” scenario, which is vastly inadequate given the IPCC’s finding that global CO2 emissions in 2050 must reach net-zero in order to limit warming to 1.5°C (IPCC, 2018).
2020 pledges
Under the Copenhagen Accord, the Russian Federation pledged to limit emissions by 15–25% below 1990 levels by 2020 (Russian Federation Government, 2010). Due to lack of clarity regarding the inclusion of the LULUCF sector in the 2020 target, in our assessment we show estimates of the resulting 2020 target emissions levels for both, excluding, and including LULUCF in the base year. Under these scenarios, the 2020 target emissions level would be 2.4 to 2.8 GtCO2e, which is 8–26% above 2018 non-LULUCF emissions.
In September 2013, the Russian Federation adopted Decree No. 752 On Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions, which set a target of reducing emissions 25% below 1990 levels by 2020. This target was reaffirmed in Decree No. 504-p in April 2014 (Russian Federation, 2014a) and is in line with the lower end of the Copenhagen Pledge’s range.
Further analysis
Latest publications
Stay informed
Subscribe to our newsletter