Pledges And Targets
Summary Table
Paris Agreement targets
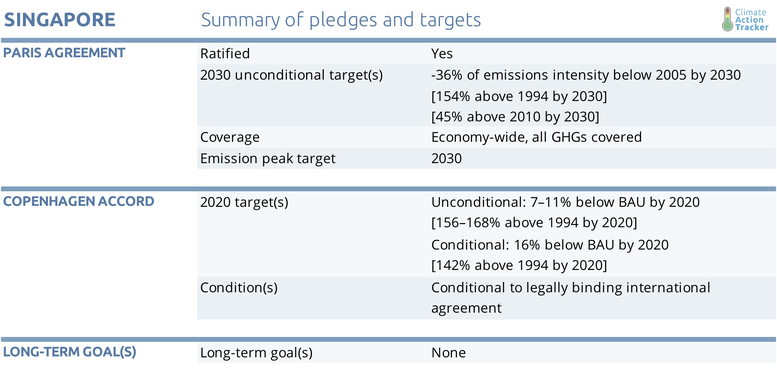
Singapore officially ratified the Paris Agreement (PA) on September 21, 2016. Its NDC target is a reduction of emissions intensity of GDP by 36% below 2005 levels (0.176 gCO2e/SGD as specified in the NDC) by 2030 and stabilising emissions, aiming for them to peak around 65 MtCO2e in 2030 (Singapore Government, 2015). Given the stabilisation levels in the NDC are reported in accordance with the IPCC Second Assessment Report Global Warming Potentials (SAR GWP), the Climate Action Tracker estimated the equivalent stabilisations levels in Fourth Assessment Global Warming Potentials (AR4 GWP) using the same underlying GDP assumptions in the NDC, getting to a target level of 68 MtCO2e (AR4 GWP) by 2030.
2020 Pledge
Under the Copenhagen agreement, Singapore committed to reduce its emissions by 7–11% below business-as-usual (BAU) emissions in 2020 unilaterally and, in the event of a legally binding international agreement, by 16% below BAU. The National Climate Change Strategy includes several unconditional mitigation targets for the same year, e.g. a 35% reduction in energy intensity from 2005 levels (National Climate Change Secretariat, 2012).
Of concern is that the BAU pathway provided by the government as reference for the 2020 target assumed the emissions intensity of the economy would go in the opposite direction from the historical trend, increasing significantly until 2020. Despite the fact the emissions intensity of GDP dropped 48% between 2000 and 2010, the BAU pathway assumes a 17% increase between 2010 and 2020.
Further analysis
Latest publications
Stay informed
Subscribe to our newsletter