Pledges And Targets
Summary table
Paris Agreement targets
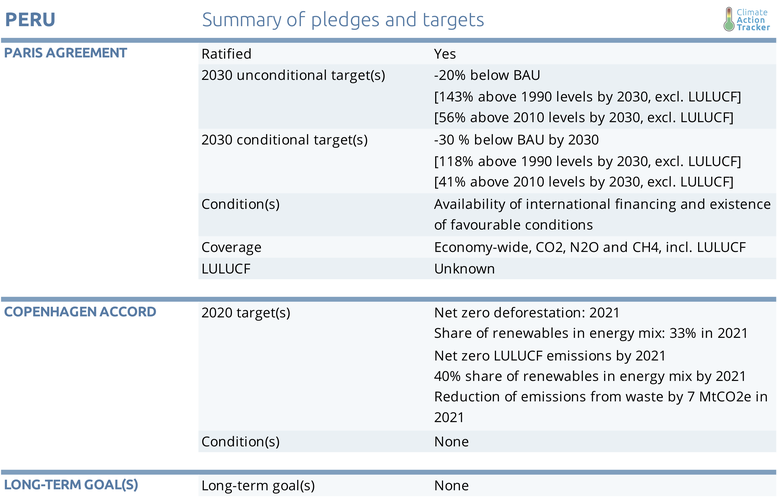
Peru ratified the Paris Agreement on 25 July 2016. In its NDC, the government of Peru proposes two targets: an unconditional reduction by 20% below a BAU scenario in 2030 and a conditional (on international finance) reduction of 30% below BAU scenario in the same year, both including LULUCF. The 2018 framework law on climate change effectively made Peru’s NDC legally binding
The 2030 emissions level under the unconditional target is 131 MtCO2e. We estimate this translates to be 143% above 1990 levels (56% above 2010 levels) and for the conditional target (118 MtCO2e in 2030) this translates to 118% above 1990 levels (41% above 2010 levels), with both estimates excluding LULUCF. For the unconditional target, the government projects that 77% of the total mitigation will be achieved in the forestry sector. The remaining 23% of mitigation will be achieved in the energy, transport, industrial and waste sectors. For the conditional target, the government projects that 71% of emission reductions will be obtained in the forestry sector
2020 pledges
Peru submitted the three pledges in the shape of NAMAs (Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions)1 under the Copenhagen accord in June 2010 (Government of Peru, 2010) which were later refined in Peru’s communication to the UNFCCC in November 2011 in the following way (GFLAC, 2015):
- To reduce net LULUCF emissions to zero by 2021,
- To increase the share of renewables in the energy mix to at least 40% by 2021, and
- To reduce emissions in the waste sector by 7 MtCO2e in 2021 (compared to the year 2000).
It was not possible to quantify the impact of these pledges, as baselines were not available. Nonetheless, the LULUCF pledge could have a substantial impact, as the LULUCF sector currently accounts for approximately half of Peru’s total GHG emissions.
These pledges are not mentioned in Peru’s NDC.
1 | Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions (NAMAs) are voluntary measures undertaken by developing countries to contribute to greenhouse gas emission mitigation. The concept was introduced 2007 at the 13th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) in Bali, Indonesia.
Further analysis
Latest publications
Stay informed
Subscribe to our newsletter